Chat now


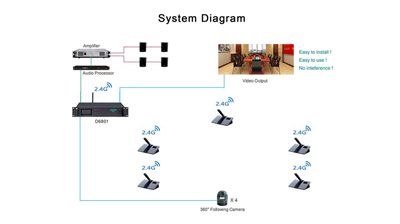

The digital wireless conference system uses a high-frequency digital radio frequency transmission chip for the transmission of voice data packet. The working frequency point is generated by the high-precision crystal oscillator and the chip, which are at the same time combined with the synchronous software verification of the transmitting and receiving ends.

Under normal use, it can permanently ensure that the working frequency of the matched transmitter and receiver will not shift. The transmitter can only work with the only registered receiver. The transmitter cannot work if the receiver is not turned on. And it is guaranteed that during work, they can be corrected at the accurate frequency point and the conference will not be intercepted to ensure the confidentiality at any time.
After the microphone picks up the sound, the sound pressure becomes an electric signal and is transmitted to the high-fidelity digital voice sampling circuit for digital processing, and at the same time, a 256-bit digital encryption algorithm is bound with the chip information to become a voice data packet to realize the confidentiality function.

The digital wireless conference system uses a sampling algorithm combining A/D software and hardware at the transmitting end to process the analog audio into data packets and transmit them through the RF radio frequency transmitting circuit; there is a corresponding RF radio frequency receiving circuit at the receiving end, which converts the received audio data packets into analog audio through the reduction algorithm of the combination of D/A software and hardware, and then outputs high-fidelity, clear, dynamic and rich analog audio through the shaping filter.

The high-frequency bandwidth resources occupied by the transmission of the digital wireless conference system are stable, and the sound size reflects the change of the data content in the data packet; the analog carrier wave is affected by the sound size, and the larger the sound, the wider the bandwidth occupied (displayed as abnormal crosstalk that occurs suddenly, and occasionally sounds from other conference rooms may be heard).
The digital wireless conference system uses the powerful MCU management function to make the 4 speaking microphones occupy one frequency point to work, and the audio of multiple transmitting microphones is tuned in sequence within the data packet clock cycle of the receiver, which completely solves the problem that multiple RF points are occupied in the conference using wireless microphone (one host with eight microphones) and avoids the cross-frequency interference caused by the secondary and tertiary intermodulation interference frequency points generated by multi-frequency point work.
 【DSPPA Demo】PAVA8000 EN54 Voice Evacuation SystemNovember 12, 2020Abstract: DSPPA PAVA8000 EN54 Voice Evacuation SystemToday, we are gonna show you a demo about our PAVA8000 EN54 Voice Evacuation System.PAVA8000EN54 Voice Evacuation System can not only support manua...view
【DSPPA Demo】PAVA8000 EN54 Voice Evacuation SystemNovember 12, 2020Abstract: DSPPA PAVA8000 EN54 Voice Evacuation SystemToday, we are gonna show you a demo about our PAVA8000 EN54 Voice Evacuation System.PAVA8000EN54 Voice Evacuation System can not only support manua...view The National Standard Approval Meeting held in BeijingJuly 19, 2019The National Standard Approval Meeting held in BeijingThe approval meeting of the National StandardTechnical standard of public address system engineeringis held in Beijing on July 16, 2019. Xue Chang...view
The National Standard Approval Meeting held in BeijingJuly 19, 2019The National Standard Approval Meeting held in BeijingThe approval meeting of the National StandardTechnical standard of public address system engineeringis held in Beijing on July 16, 2019. Xue Chang...view